CryoSPARC v5.0.0
Changes to CryoSPARC’s Software System and Dependencies in v5
In v5, CryoSPARC’s underlying software system has been completely redesigned for stability, scalability, and to enable future developments. The new system adds strong validation and consistency guarantees for CryoSPARC database contents.
CryoSPARC v5 is backwards compatible with v4 versions, meaning:
- A v4.0+ instance can be upgraded to v5, and also downgraded back to v4.4+ if needed
- Projects detached from v4 instances can be attached to v5 instances, and vice versa
Updating to CryoSPARC v5 will perform a dry-run phase to validate all database contents and will take some time, up to one hour for large instances. The user interface will not be available during the update process.
Please review compatibility notes below and full update instructions here.
Compatibility Notes
For CryoSPARC v5, the operating system must support GLIBC 2.28 or greater. Therefore, the oldest compatible operating systems are Rocky/RHEL 8 and Ubuntu 20.04. However, Ubuntu 22.04 or newer is recommended.
CryoSPARC v5 requires NVIDIA driver version 570.26 or newer. Note that NVIDIA Blackwell devices are only compatible with the open driver. CryoSPARC v5 uses CUDA 12.8 which drops support for NVIDIA GPUs with compute capability 3.5 (Kepler). Only GPUs with compute capability 5.0 (Maxwell) to 12.0 (Blackwell) are supported.
A new, backwards compatible version of cryosparc-tools for scripting with v5 is available; see details here. Scripts written with previous versions will continue to function as before.
CryoSPARC v5 introduces a new improved command line interface that is not compatible with v4 cli commands. Scripts that used v4 cli commands will need to be updated, including for managing CryoSPARC Live sessions.
At a Glance
CryoSPARC v5 BETA
Dozens of features, improvements and fixes
Dashboard and Comparison View
Visualize how results change over time and compare between jobs
In-App Documentation Links
Direct pointers to key pages in the CryoSPARC Guide
Ab-Initio Refinement
Reconstruct to high resolution preserving gold standard split
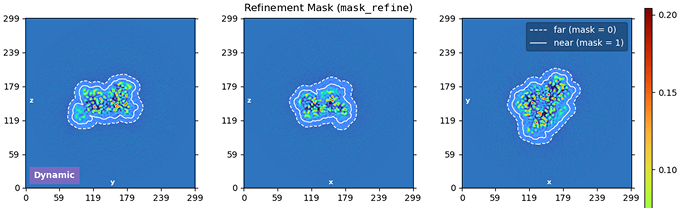
3D Masking Overhaul
New dynamic masking that reduces the likelihood of overfitting
Live Workflow Improvements
Delay start, auto-pause and multiple workers per GPU
Collapsible Upstream Jobs in Tree View
See only the jobs relevant in your workspace
Copy and Paste Parameters
Quickly transpose parameters to another job
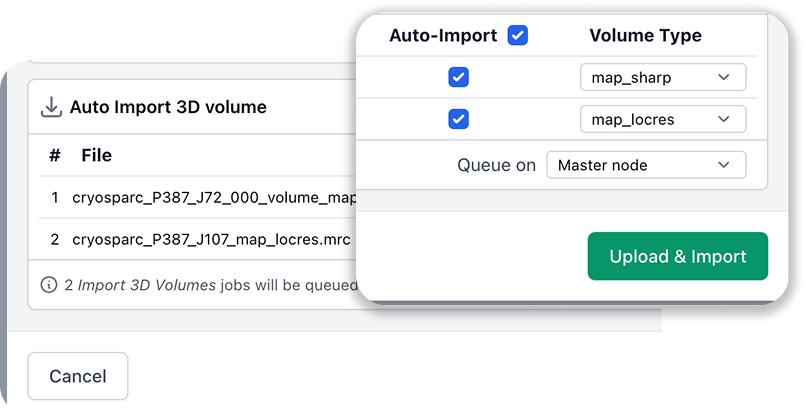
Auto-Import 3D Volumes
Automatically import .mrc and .map files when uploading
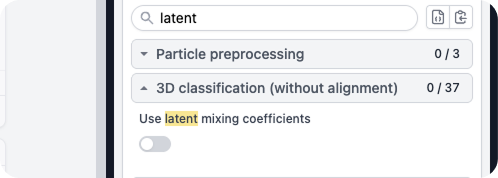
3D Classification Advanced Parameters
Enable latent mixing coefficients for rare classes
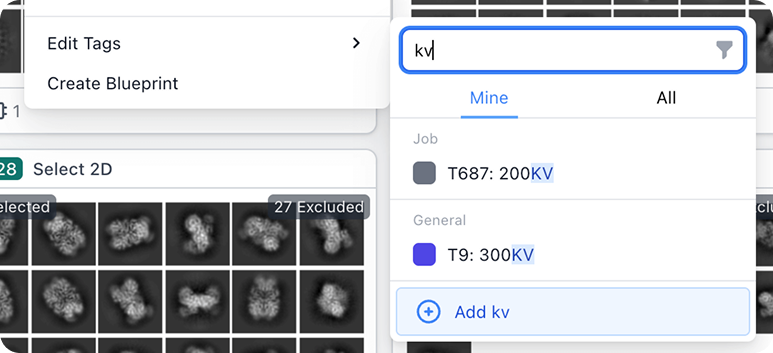
Upgraded Tagging
Tag multiple jobs, inline creation, improved management
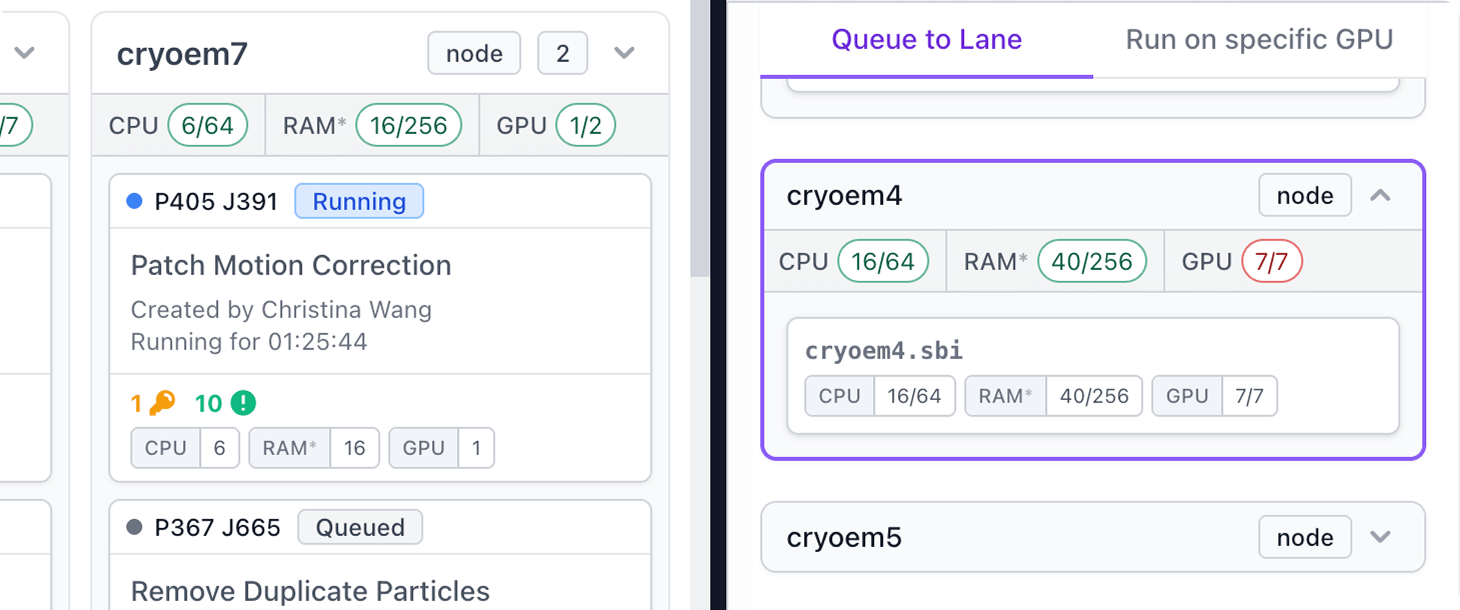
Improved Resource Visibility
See GPU/CPU/RAM allocation across the interface
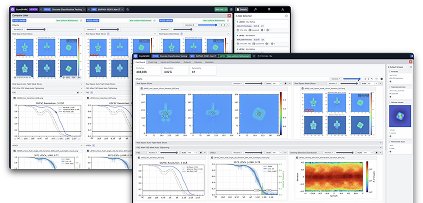
Job Dashboard and Comparison View
The Job Dashboard displays all key job outputs, plots, and statistics at a glance, and is the new default view when opening a job card. Use iteration sliders to see how results and plots changed during processing.
Multi-select jobs and press spacebar: The Comparison View shows all selected jobs’ parameters, outputs, and plots side-by-side, making it easy to spot differences and make decisions about the effect of input or parameter changes. Use iteration sliders to visualize progress, and download outputs from multiple jobs in one click.
Overhaul of 3D Masking in Refinements
CryoSPARC v5.0 introduces a new automatic mask generation method that is robust across a wide range of resolutions and reduces the possibility of overfitting or overestimation of resolution, without users having to adjust masking parameters.
- Dynamically generated masks now use mask tightness and softness parameters that are based on the 3D refinement map's current resolution estimate, meaning that masks for lower-resolution structures automatically have softer padding.
- The new method is used for refinement masks (
mask_refine) and resolution masks (mask_fsc), and makes it significantly less likely that user-set masking parameters produce masks that are too tight or too hard, especially for low or moderate resolution structures. Mask auto-tightening has also been made more conservative by default. - Across all refinement jobs, both the refinement and the resolution masks are plotted each iteration, in a new plot that displays the extent of the mask edge falloff.
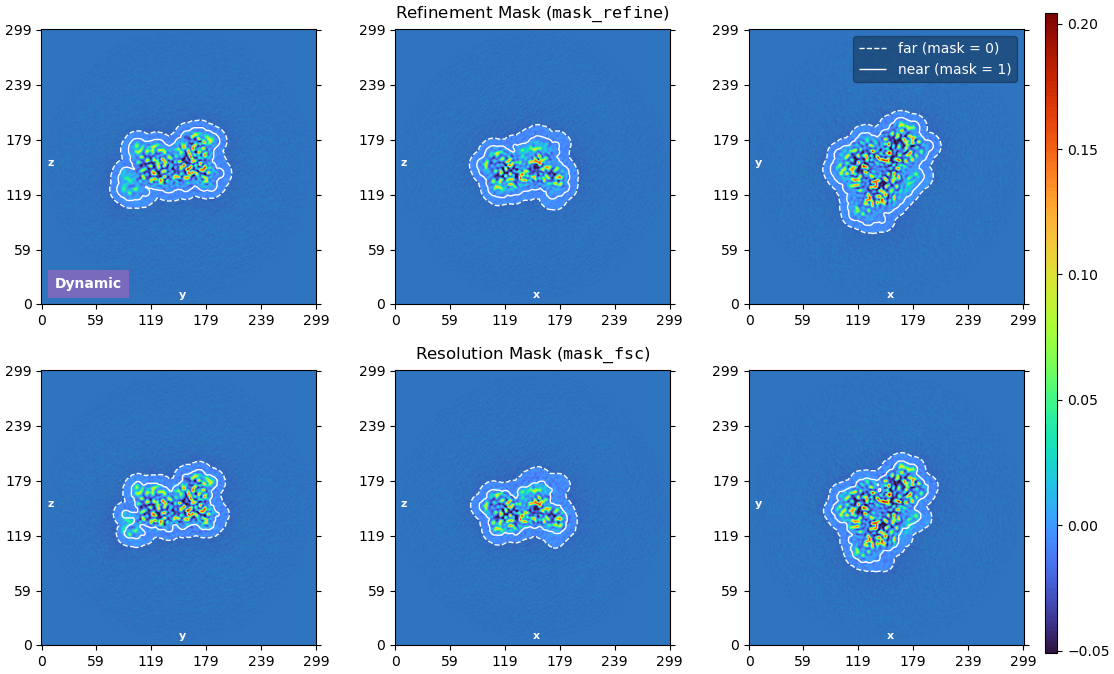
Refinement jobs now have a parameter “Use dynamic refinement mask” that can be turned off to allow the job to run without any refinement mask applied during iterations. In some cases, especially in Non-Uniform Refinement, using no mask can produce improved results.
All refinement jobs now output the refinement mask, resolution mask, and auto-tightened resolution mask as separate draggable outputs.
Standardized FSC Plots and Outputs
FSC curve plots are now standardized across CryoSPARC, with a consistent colour scheme that more clearly indicates which mask has been used to produce each curve, and whether correction via phase randomization has been applied.
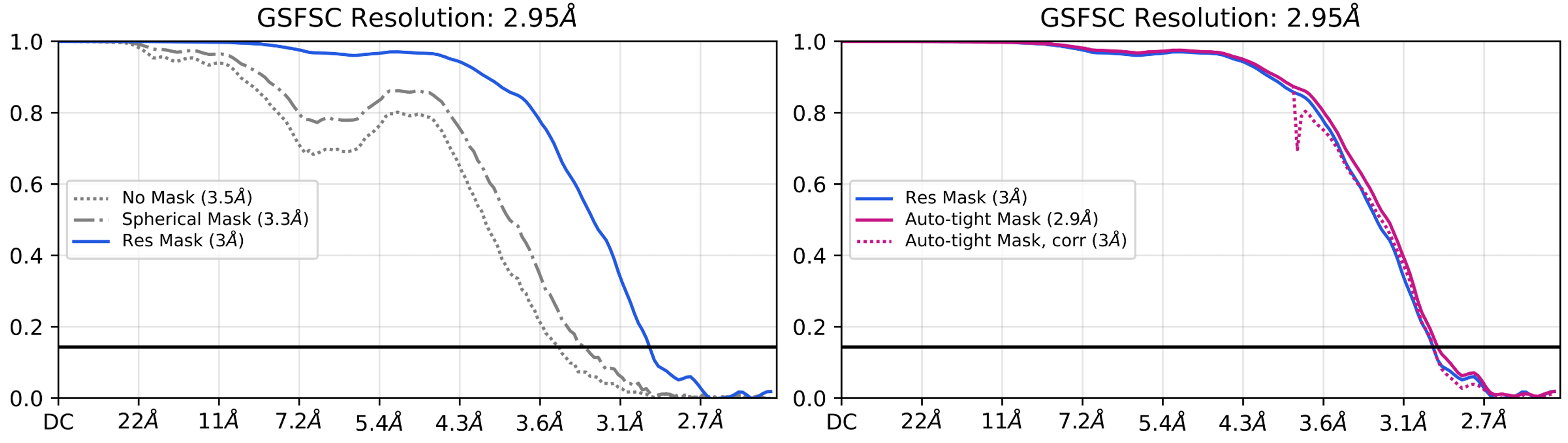
If FSC resolution meets or exceeds the Nyquist frequency, refinement jobs now throw a warning to recommend re-extracting particles with a smaller pixel size.
The format of FSC txt files has been updated to include additional columns and column titles.
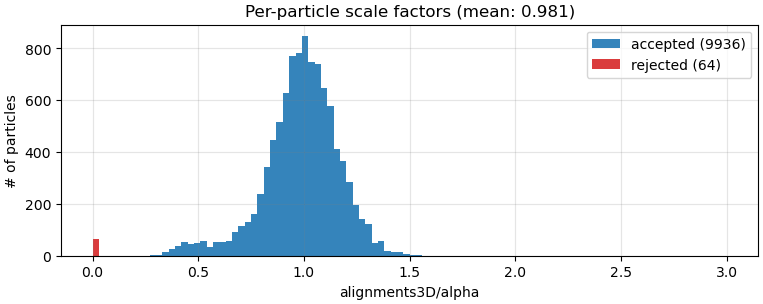
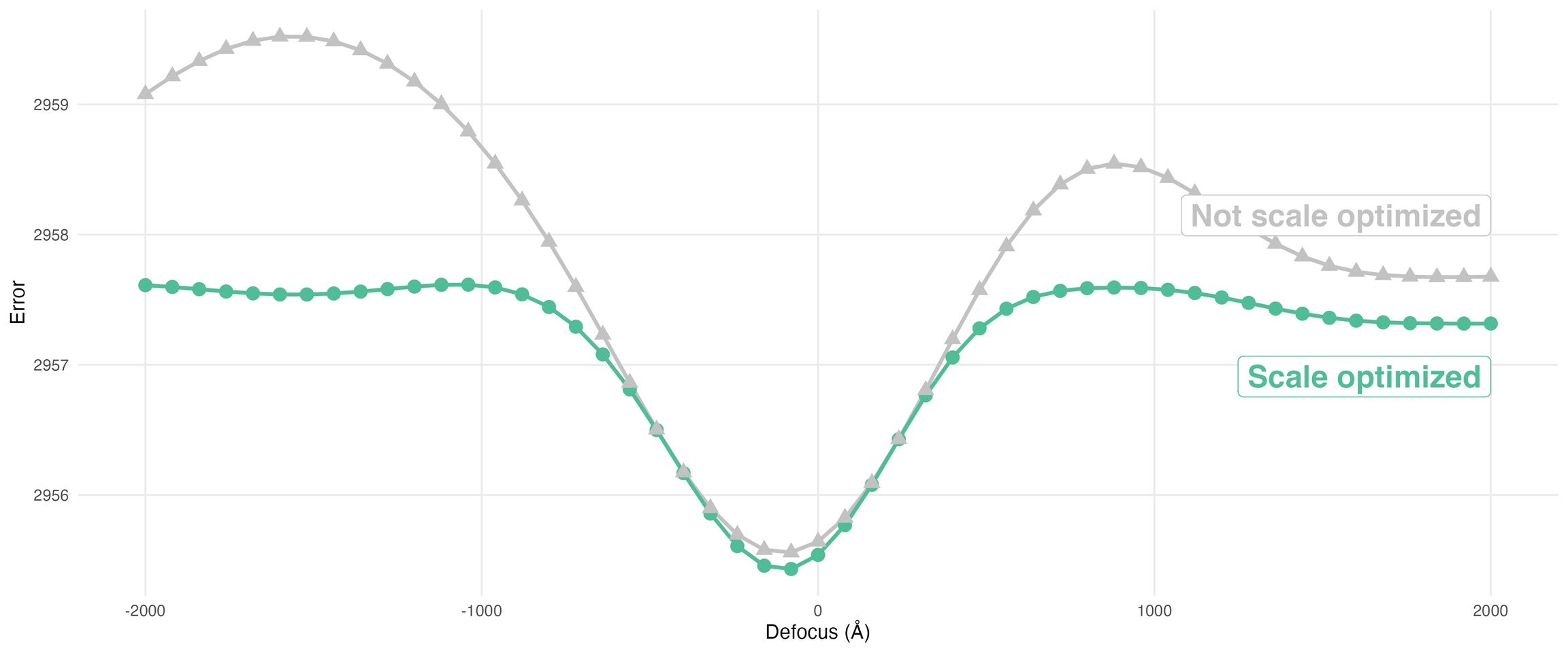
Per-particle Scale Optimization in Refinements
By default, refinements (Homogeneous, Non-uniform, and Helical) now perform per-particle scale optimization. The optimized values provide a measure of particle quality, which is used during 3D reconstruction to down-weight low quality particles. The per-particle scale values can also be useful for separating low-quality particles from a dataset.
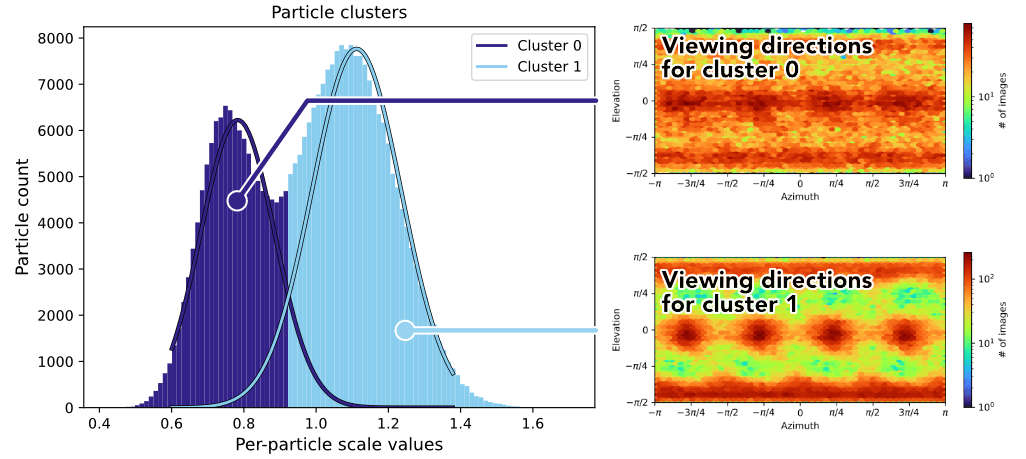
All refinements, Local CTF Refinement, 3D Classification, and 3D Variability Analysis now create a Rejected Particles output group. The group is populated with particles that had zero or negative per-particle scale, indicating empty or inverted contrast that is ignored during 3D reconstruction.
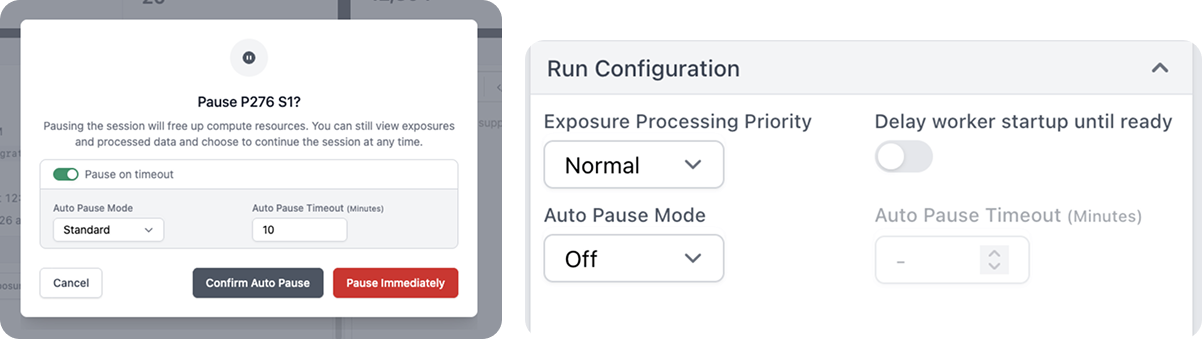
CryoSPARC Live Workflow Improvements
The new Run Configuration options in CryoSPARC Live enable auto-start and auto-pause of Live Sessions to better match data collection workflows. Multiple sessions can be started at the same time, each pointing to a different raw data input directory (e.g., corresponding to multiple grids). Sessions can be started with Delay worker startup until ready so that Live Preprocessing worker jobs will not launch until new data is detected. Auto pause mode triggers when no new data has been detected for a configurable timeout and automatically pauses Sessions to free up GPU and license resources for the next session.
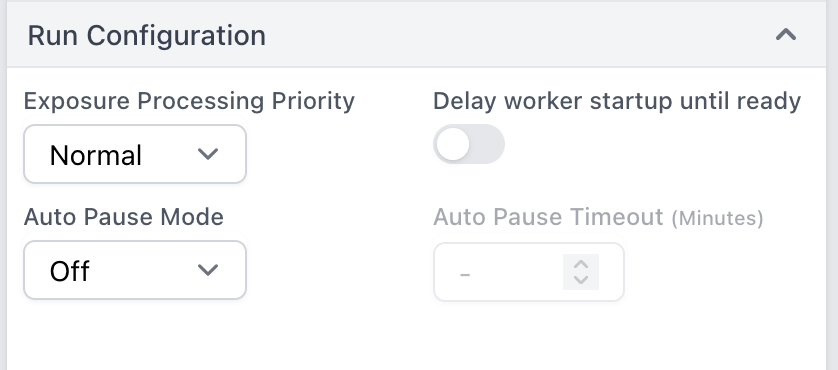
Auto Pause Mode automatically pauses the Live Session when there are no remaining exposures to process, with two available modes:
- Standard: Pause the session immediately after the idle timeout has expired. This will kill any running 2D/3D streaming jobs at the time auto pause is triggered.
- Graceful: Once the idle timeout has lapsed, also wait for 2D/3D streaming jobs to finish processing the available particles before pausing the session.
- An
Auto Pause Timeoutcan also optionally be configured.
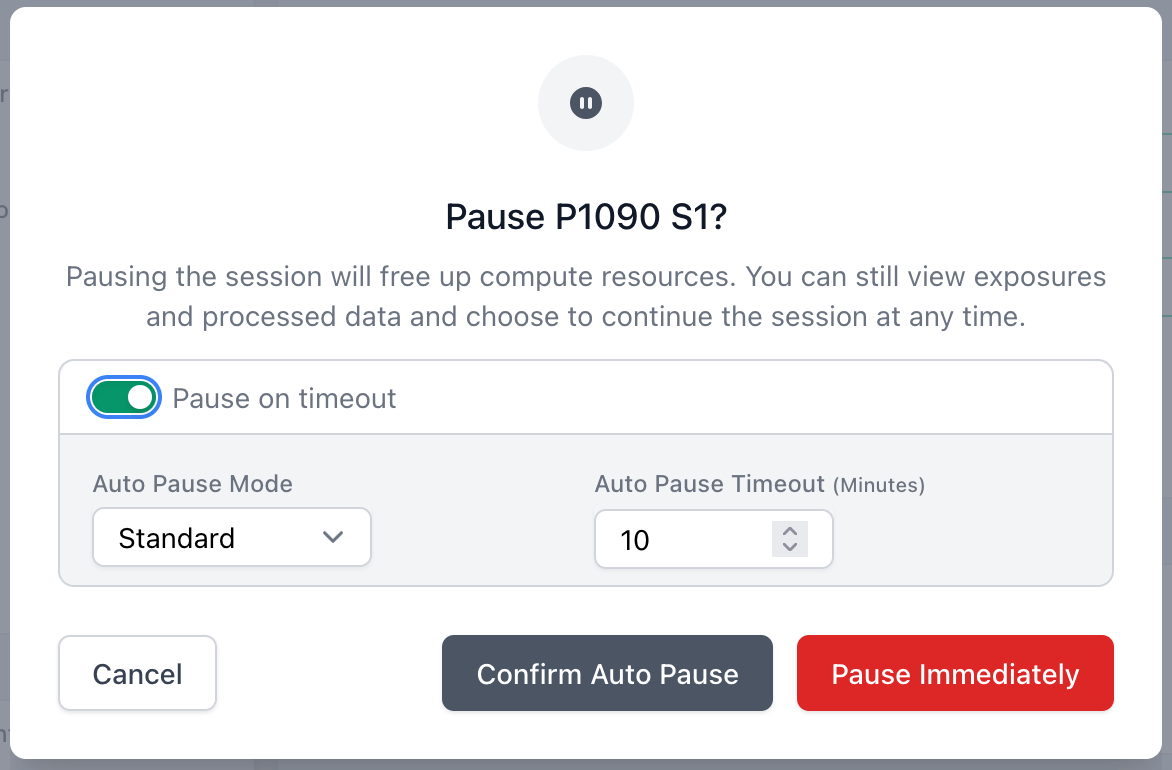
Ability to launch more than one Live Preprocessing worker job per GPU. Use Workers per GPU in the Configuration Tab to specify the number of Live Preprocessing worker jobs to launch per GPU worker. On some systems, running multiple workers jobs per GPU can improve preprocessing throughput.
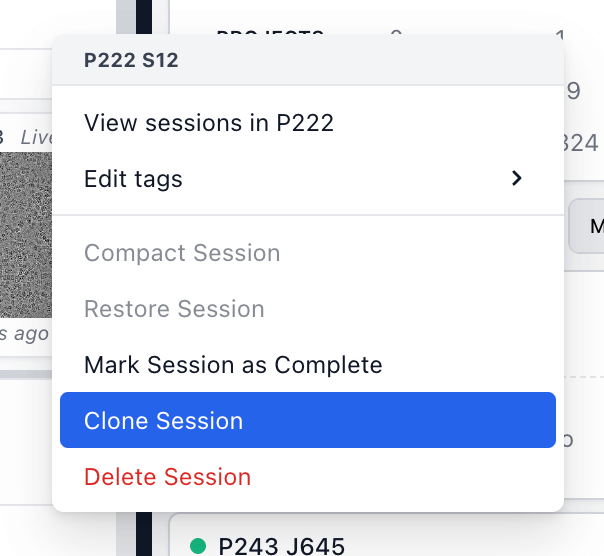
Live Sessions can now be cloned in the UI. Cloning a session preserves configuration.
CryoSPARC Live Sessions will now inherit the project-level parameter for outputting in 16-bit floating point format.
Exposure filenames in Live now correctly pad UIDs with leading zeros.
The Live particle export job's output is now correctly named "Exported Particles".
Lane selections in CryoSPARC Live now display only those of which are available for the current user.
CryoSPARC Live's configuration profiles in v5 are not backwards compatible. New profiles can be created in v5 but will not be retained if downgrading to v4.
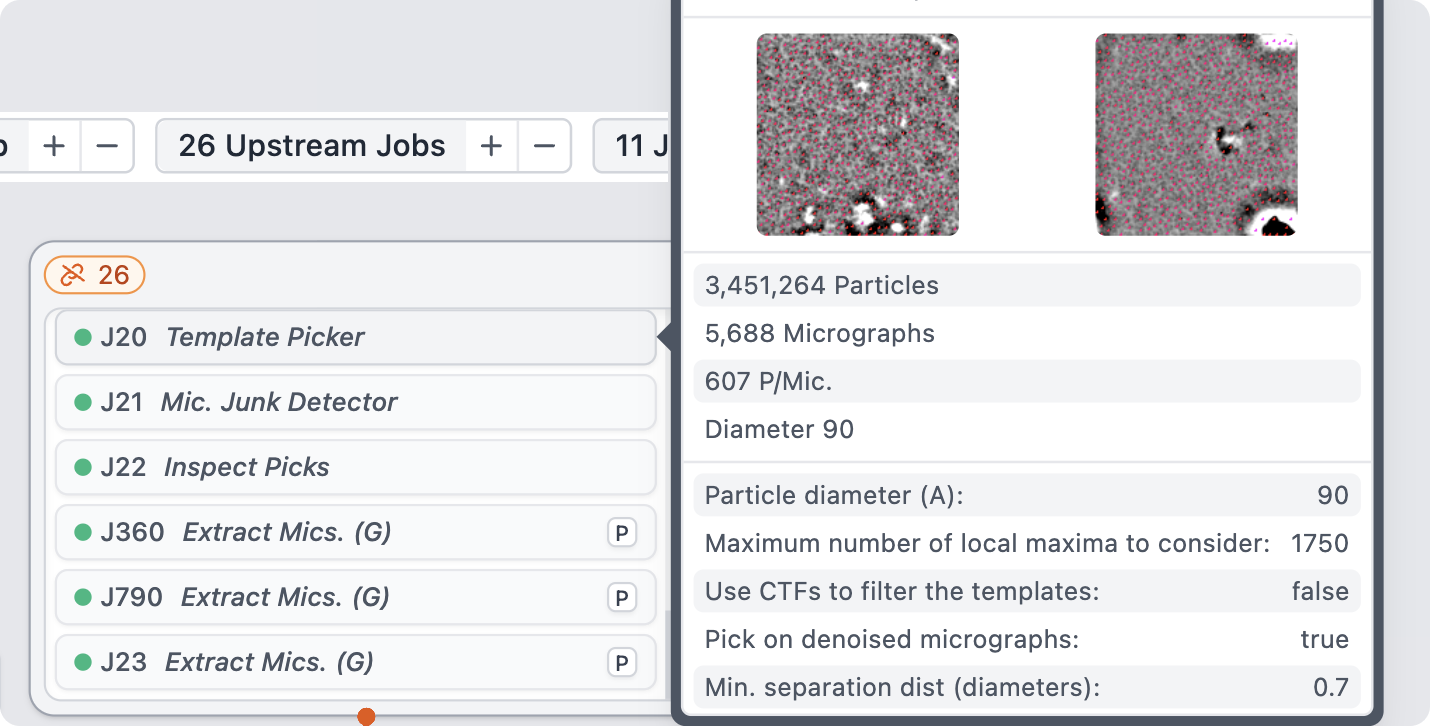
Collapsible Upstream Jobs in Tree View
Upstream jobs in the tree view will now be collapsed into single grouped cards by default, making it easy to see where jobs from other workspaces are connected to jobs in the current workspace tree. Extremely large processing trees can be condensed to display only the jobs relevant in the current workspace.
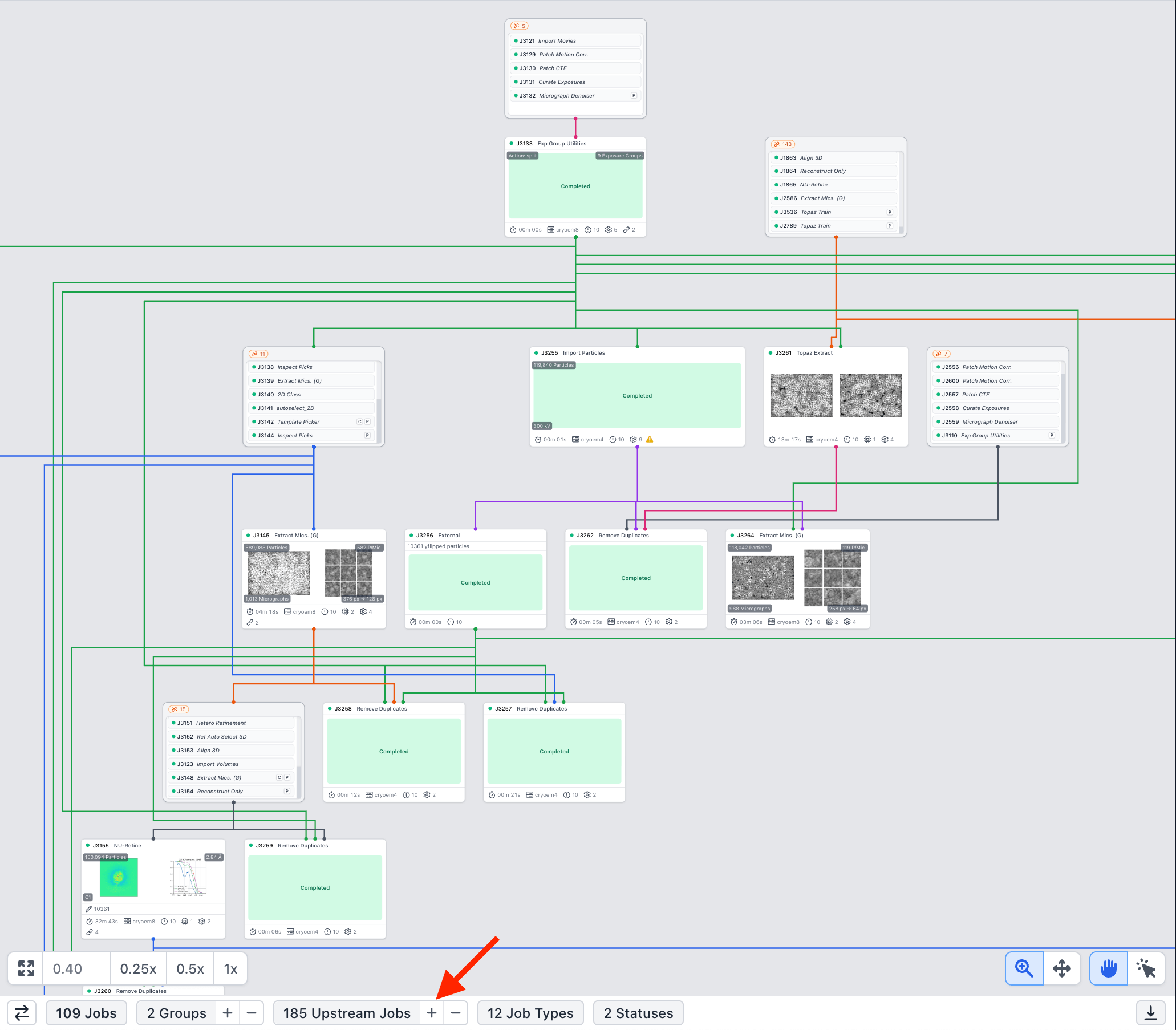
Job Group cards now list their contents; hover over any job to view its specific details.
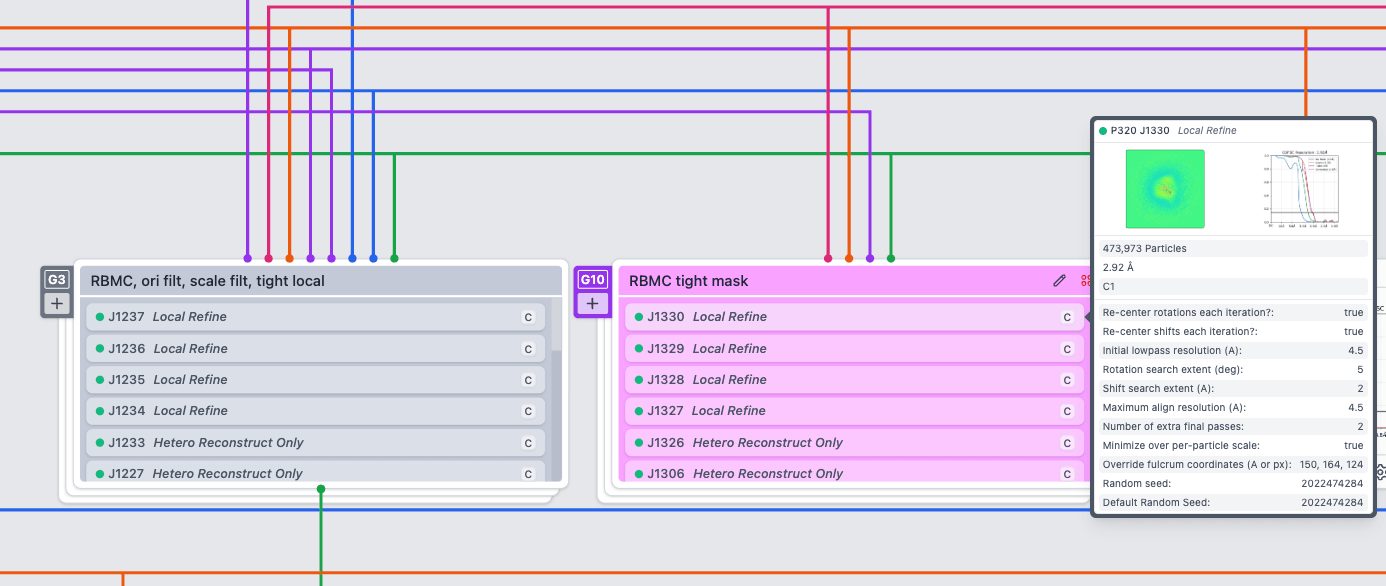
Groups in the tree or card view will no longer accept the addition of jobs that would cause a circular connection error when the group is collapsed.
Moving or unlinking jobs in the middle of a chain in the tree view will no longer cause data loading and/or layout issues in some cases.
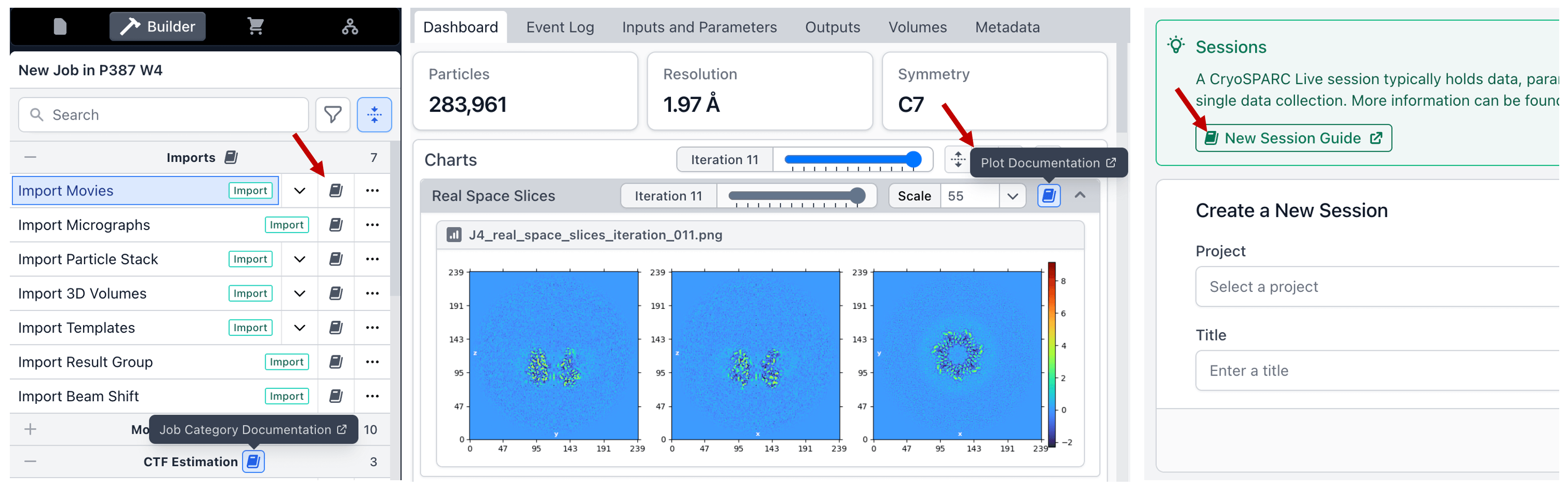
Embedded Documentation Links
Documentation icons have been added across the application that link out to relevant pages in the CryoSPARC Guide. These include documentation for core actions as well as CryoSPARC jobs, plots, and general onboarding.
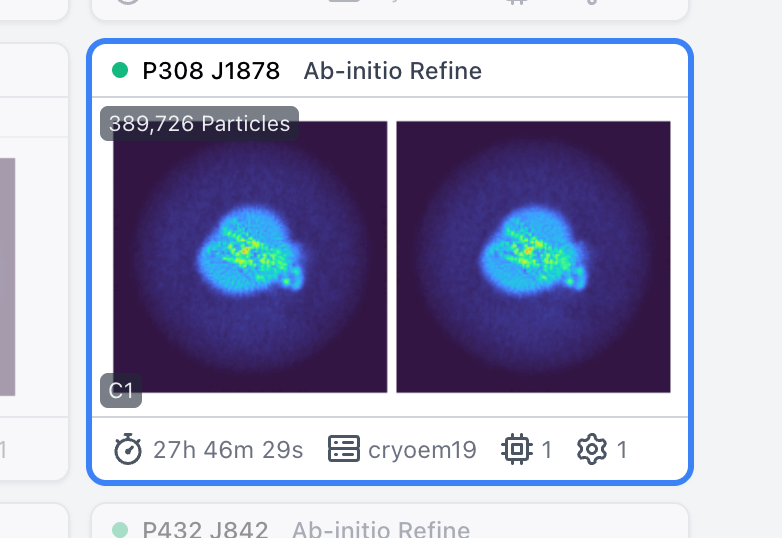
Ab-Initio Refinement to High Resolution
Homogeneous Ab-Initio Refinement (BETA) uses the same algorithm as Ab-Initio Reconstruction (i.e., stochastic gradient descent) to refine a dataset to high resolution from scratch, while preserving gold standard independence of two half-sets and half-maps. Half-maps are aligned in 3D during optimization to keep them in register. The job type is inspired by recent results showing that Ab-Initio Reconstruction can produce improved map quality for small and challenging targets when run at high resolution (HR-HAIR: Kim et al. 2025).
Local Refinement now has an option to use input half-maps for initialization, allowing local refinement to retain the gold-standard separation of half-maps from an upstream Ab-Initio Refinement or other source.
Ab-Initio Reconstruction now supports spherical or cylindrical windowing of volumes during reconstruction, via the Volume window mode parameter. Window size can be controlled with Window inner diameter and Window outer diameter parameters. Spherical windows can help with reconstruction of smaller particles, and cylindrical windows with helical particles.
Ab-Initio Reconstruction now has a parameter Minimum alignment resolution that performs high-pass filtering on the volume (for the purpose of alignment only).
Fixed a bug in Ab-Initio Reconstruction that could cause NaN errors when class volumes were near empty.
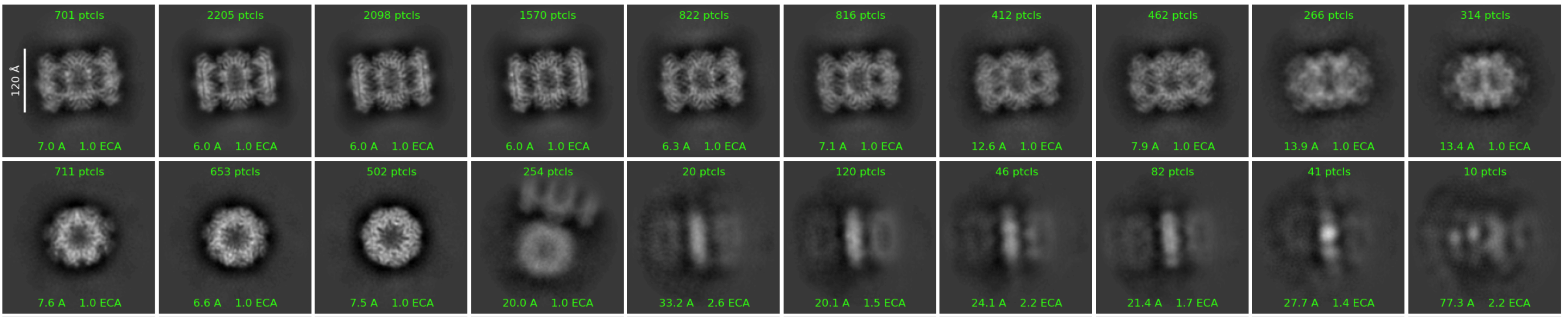
2D Classification Sorting and Fixed Alignments
2D Classification now aligns 2D classes to each other and plots classes in a sorted order determined by inter-class similarity, for easier visual comparison. This can be reverted to sorting by size, by modifying the "Plotting sort method" parameter.
Added a "Do orientation alignment" parameter to 2D Classification, turned on by default. If 3D alignments are available in input particles, this parameter can be turned off to allow for 2D Classification without alignment.
Added class index to sort options in Select 2D Classes.
3D Classification Advanced Options
3D Classification now includes the option (default: off) to use latent mixing coefficients during classification. When turned on, 3D Classification treats the current class sizes at a given iteration as a representative example of the underlying, true class sizes; formally, it applies a prior over class posteriors based on the current sizes of classes. This can result in more diverse class sizes, reducing the likelihood of 'uniform' class distributions.
In 3D Classification, the solvent mask is now automatically expanded to ensure it always fully contains the focus mask. Furthermore, if a solvent mask is not provided as input, there is a new option to Generate solvent mask from consensus (and a spherical mask is used if this option is turned off).
3D Classification now has a new real-space slice plot with improved contrast and a modified colourbar.
CTF Refinement with Per-Particle Scale
Local CTF Refinement now optimizes over per-particle scale and defocus in tandem. In testing, this can lead to better error landscapes and potentially improved defocus values.
Improved Tagging and Autosaving Job Titles
Upgraded tagging experience: quickly create and manage tags.
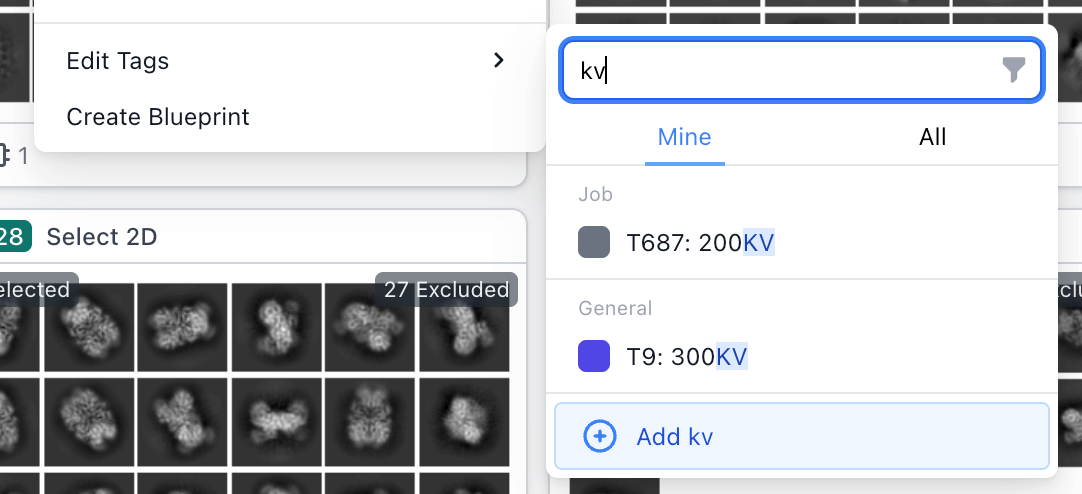
- The "Edit Tags" menu for jobs now by default only shows tags created by the current user, with a toggle to view all tags in the instance.
- Added ability to tag multiple jobs at once using the multi-actions menu.
- Added new option to create a tag in the "Edit Tags" menu. Default tag will be created with the search term if applicable, or the "Create Tag" slideover will be opened to complete creation.
- Updated tag filter in jobs browse view to only show tags that have been applied to jobs in the view.
- Redesigned tag manage dialog panel for more information density and added ability to delete multiple tags at once.
Titles and descriptions in the details sidebar autosave when edited.
Auto-Import from Local File Upload
Upload Local Files now offers the option to automatically create and queue an Import 3D Volumes job for each volume when uploading .mrc or .map files if Auto-Import is checked off. The Volume Type dropdown (map_sharp, map_locres, etc.) will be automatically populated based on the file name.
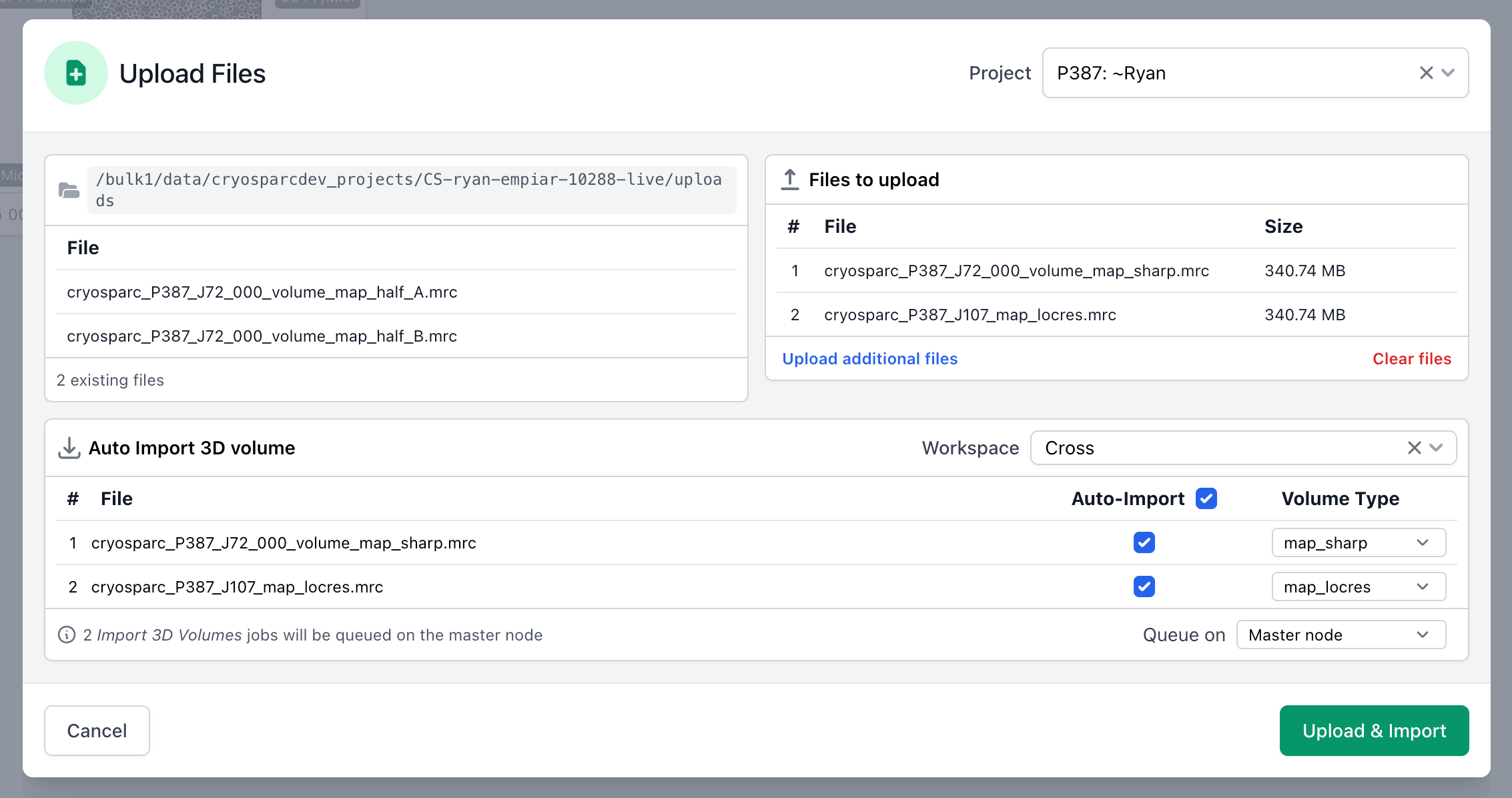
Upload Local Files provides a message when attempting to upload an unsupported file type and lists the applicable file types that are allowed.
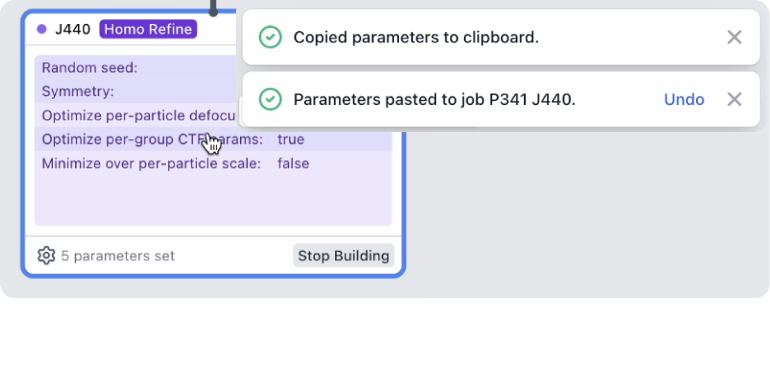
Copy/Paste Parameters and Simpler Job Creation
Copy/Paste Parameters: Use command+option+c to copy parameters from a selected job, and command+option+v to paste onto a selected job.
- Parameters can be pasted onto jobs of different types, useful between jobs with many of the same parameters such as 3D refinements.
- Parameters are copied to the clipboard as a valid CryoSPARC Blueprint, in JSON format for editing or sharing. These can also be copied from the job builder using the "Copy as Blueprint" button or
command+option+c. - Parameters can also be copied in plain text for pasting into lab notebooks, using the "Copy all parameters as text" option in the job builder.
Ability to search for parameters in the job builder.
When dragging an output group into a building job, there is now an option to replace the existing group connection if only one connection is allowed.
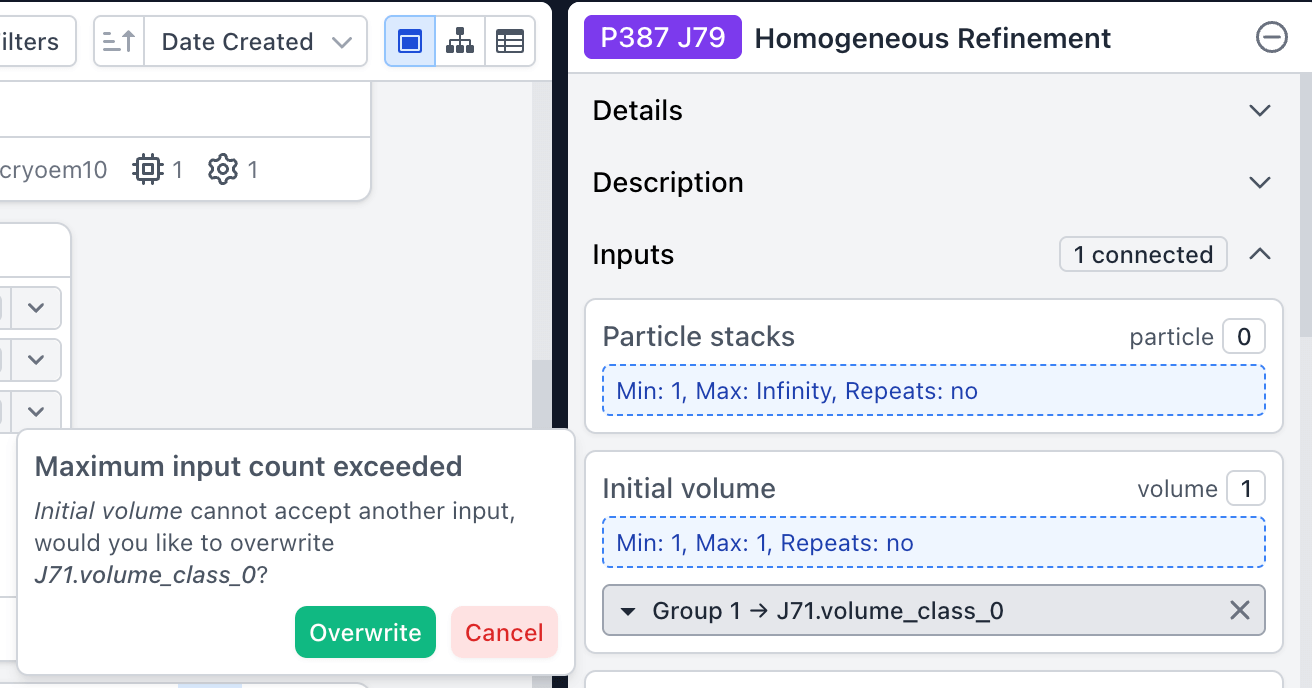
Added additional checks when building jobs to prevent incorrect number of input groups from being connected.
Prevent workflows from being applied if they are missing parent connections, preventing jobs from being connected with missing passthrough outputs.
Job Queuing and Resource Management
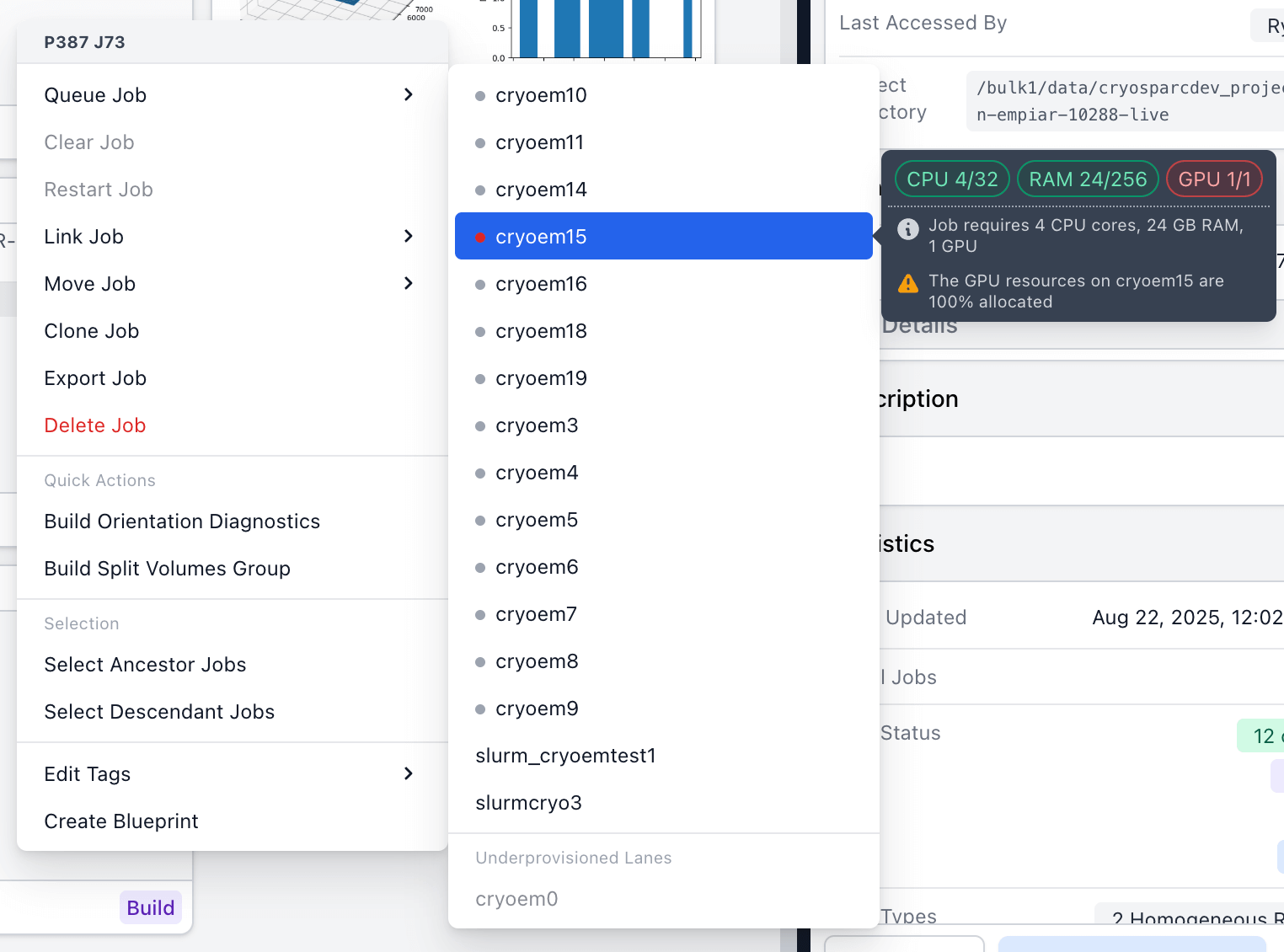
Ability to queue GPU and CPU jobs to a hostname/target directly in the Queue slide-over, plus improvements to right-click queue menu:
- The Queue slide-over now shows a warning when the CPUs, GPUs or RAM of the selected lane/target are fully allocated.
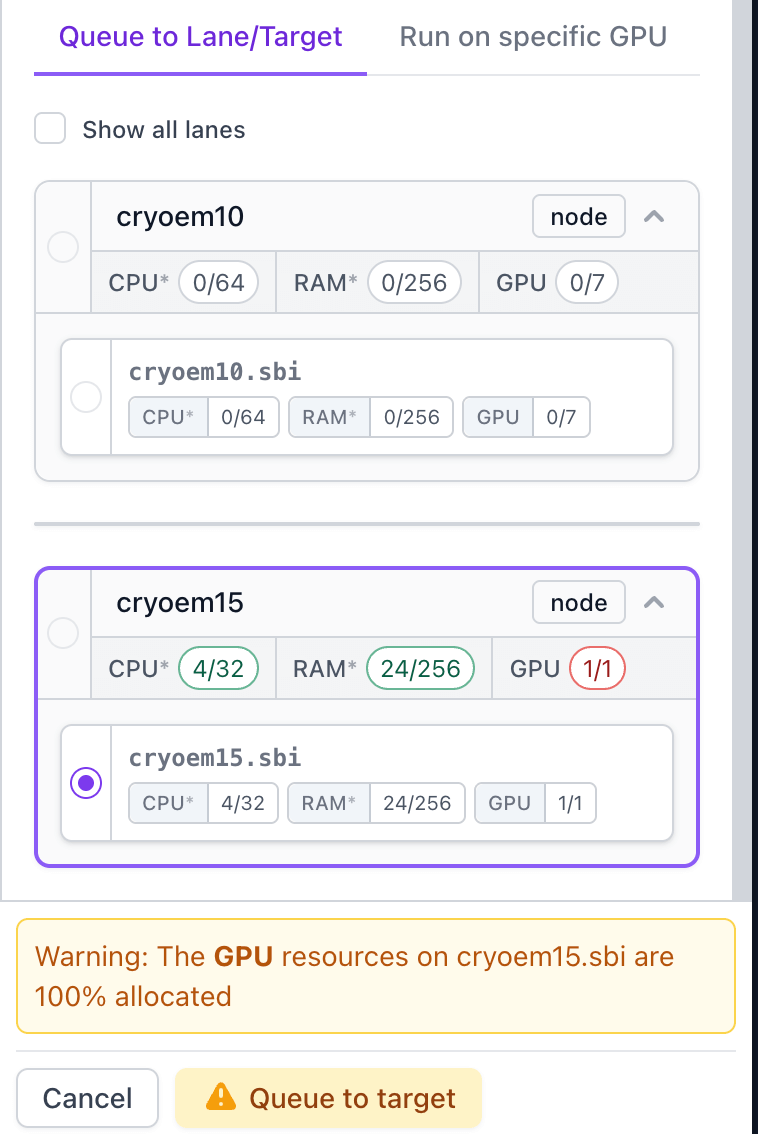
- When right-clicking on a job, the quick access menu displays a coloured light icon and tooltip for each lane's current resource allocation, the compute requirements of the job, and a warning if one of the lane's compute resources is fully allocated. Lanes with insufficient resources for the job will appear under "Underprovisioned lanes".
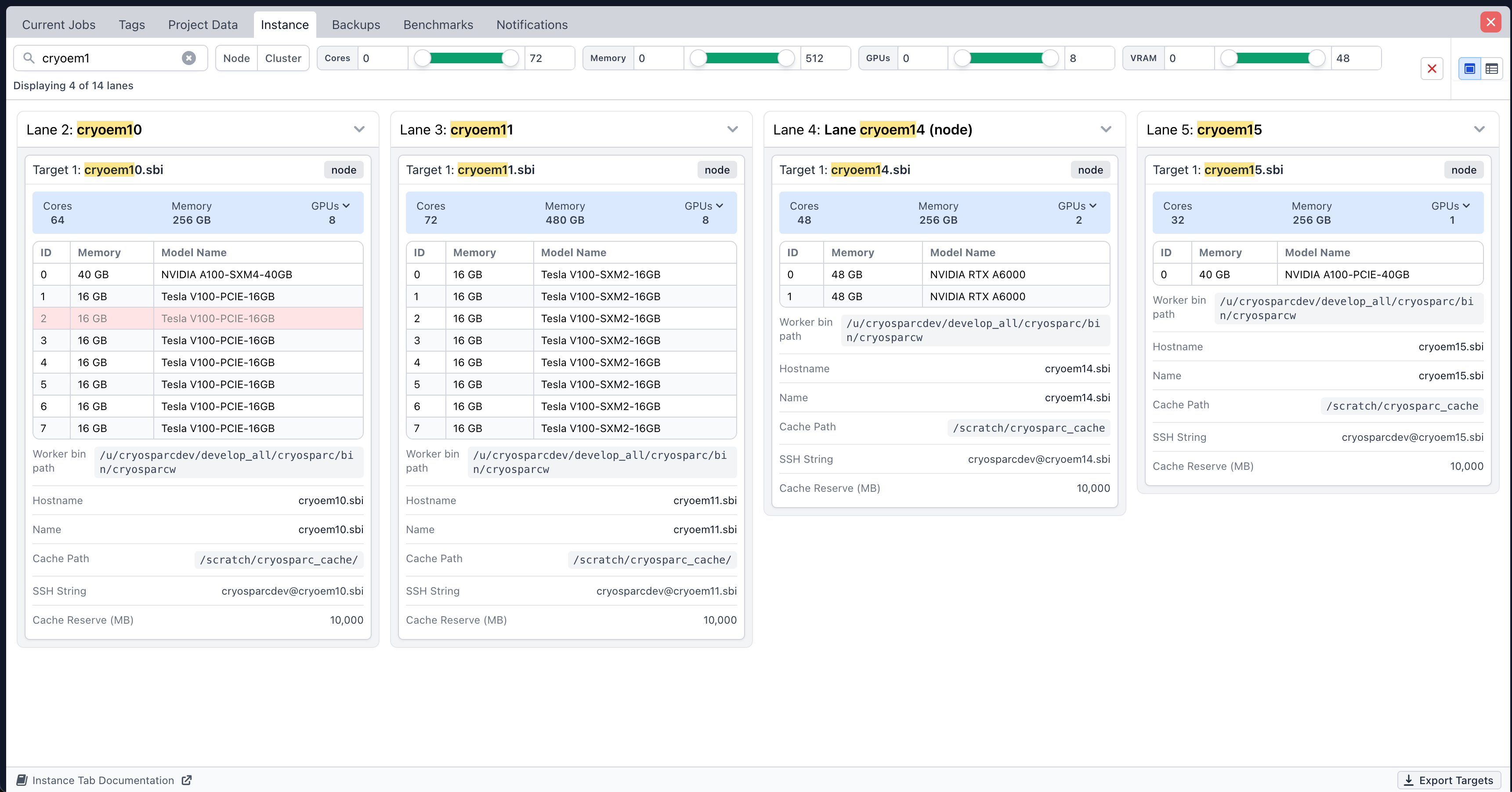
The Instance Information tab, that displays all available worker and cluster lanes, has been redesigned.
- Search filters have been added, allowing the user to filter lanes by name, lane type, and compute resources.
- Each target card now contains a list of GPUs displaying their ID, name, and VRAM.
- A new table view has been added that displays instance information in a collapsible nested tabular format.
- Contents of target paths and cluster submission scripts can now be copied to the clipboard with a single click.
- JSON export of all targets can now be downloaded.
The Current Jobs dialog and Queue slide-over now display how many compute resources (CPUs, GPUs, RAM) are currently allocated in a lane, target, or job.
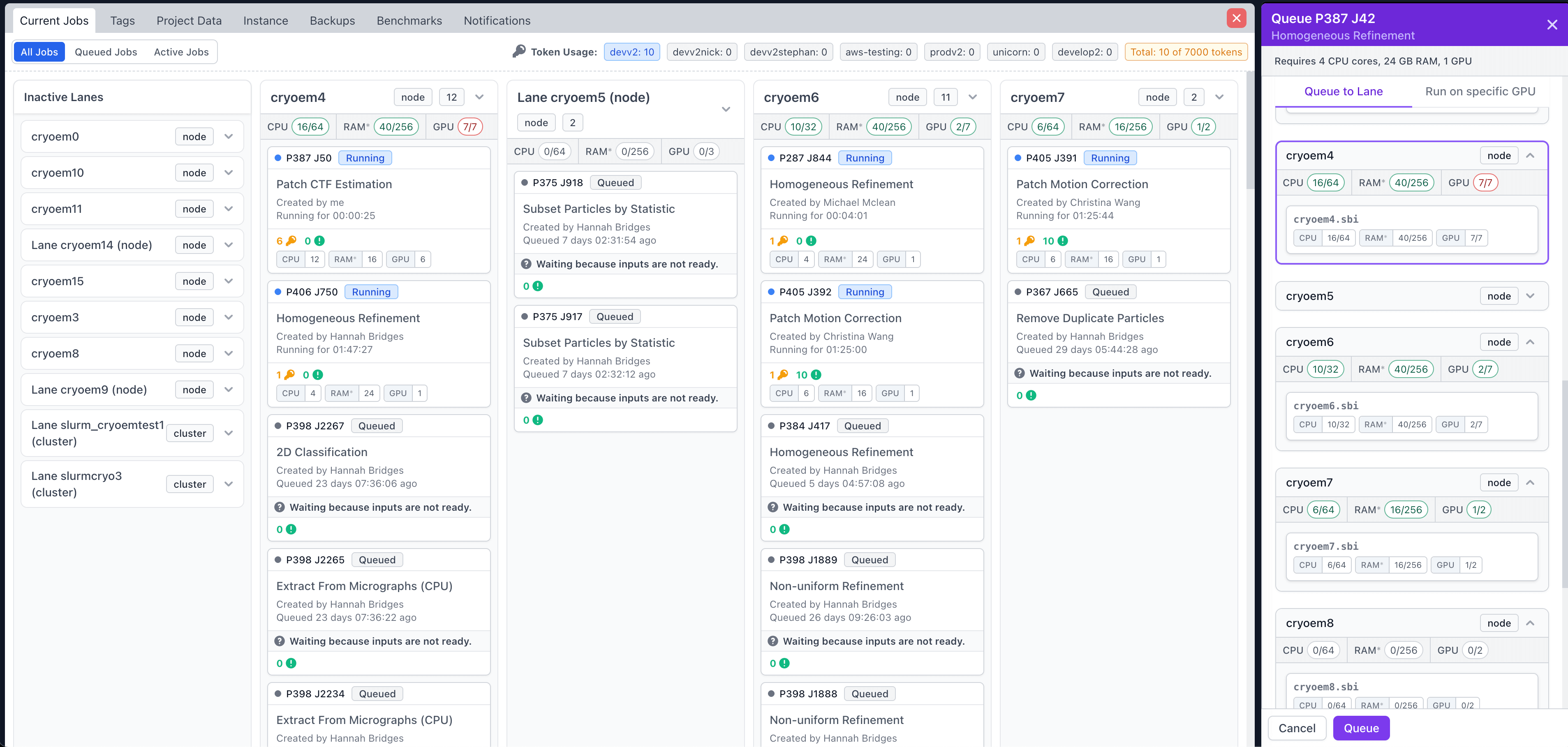
Job priority is now displayed on job cards.
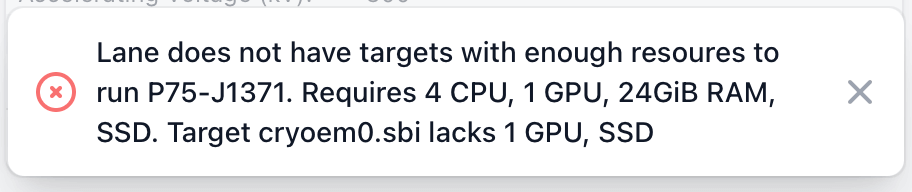
Improved error messages when queuing to under-provisioned lanes or targets.
When launching a job directly on GPUs, the list of available GPUs now respect instance configuration, hiding GPUs that are marked as unavailable to CryoSPARC.
Downloading and Exporting Reports and Metadata
Added an 'info tags' option to the job CSV download, enabling access to the same statistics presented on job cards.
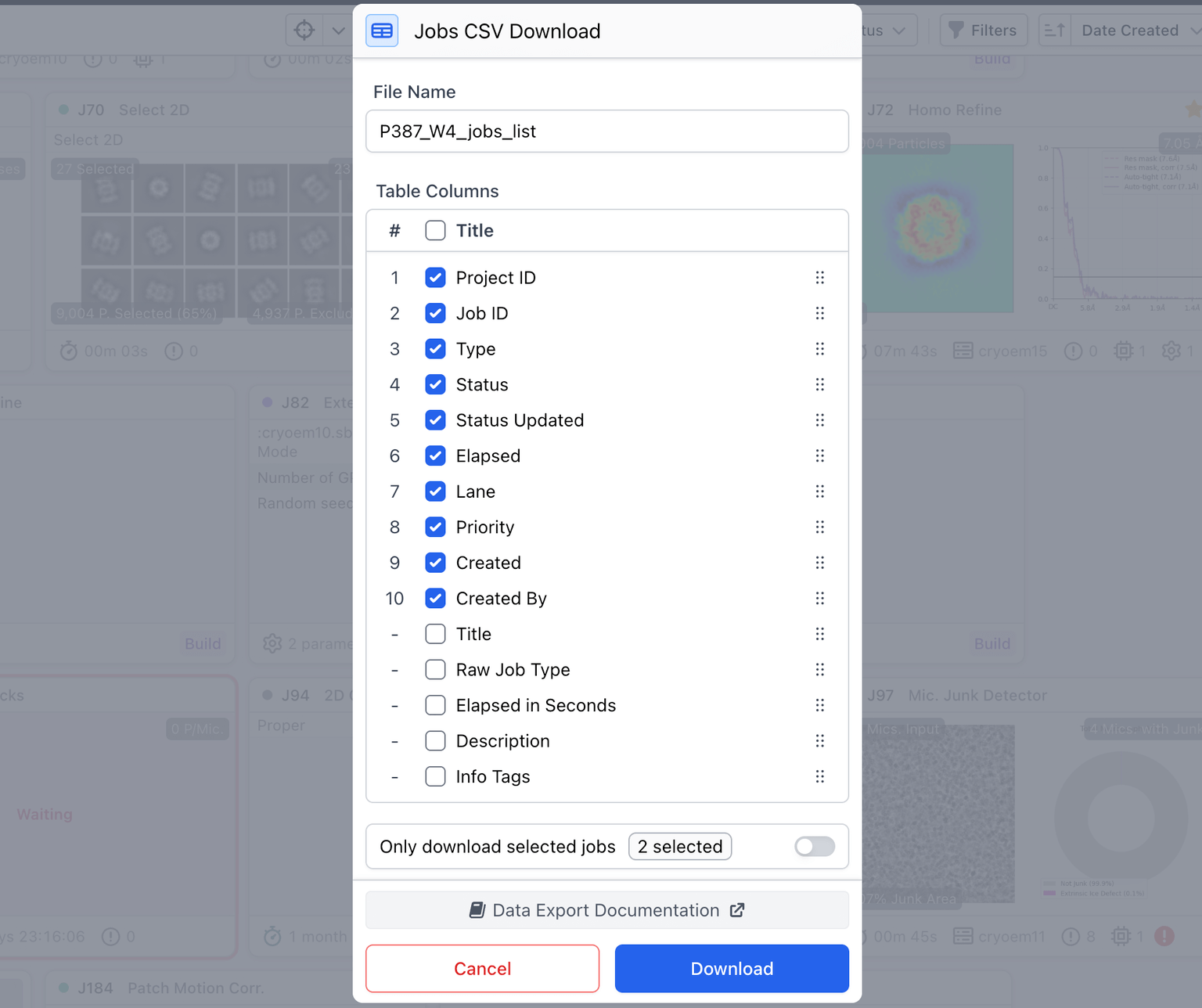
Option to download a CSV of just the selected jobs via the browse pages.
Improved job info tags and dashboard cards for Extract from Micrographs (including display of F-cropped box size and output pixel sizes), Subset Particles by Statistic and Helical Refinement.
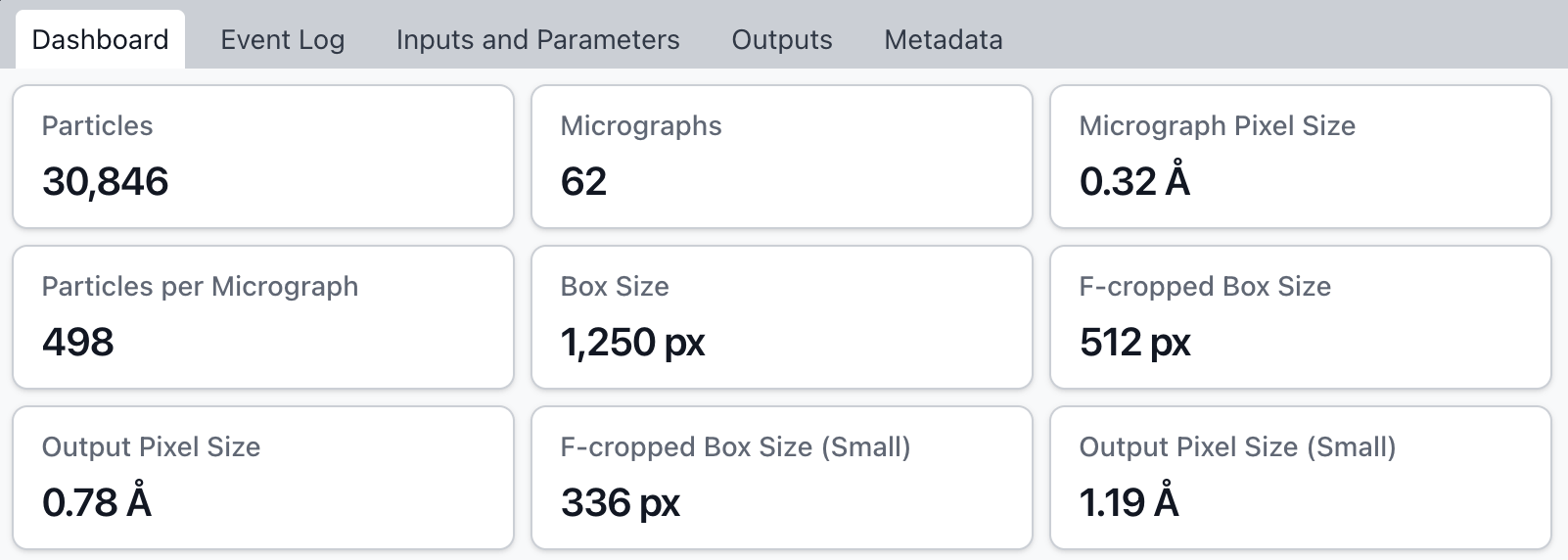
Resolved an issue where the job report would fail to download for certain jobs that contained special characters in their event log output, title or description.
Keyboard Shortcuts
The shortcuts dialog has been reworked to show all available keyboard shortcuts inside of hierarchical sections in a single panel. To open the shortcuts dialog, click on the "keyboard" icon in the left navigation bar.
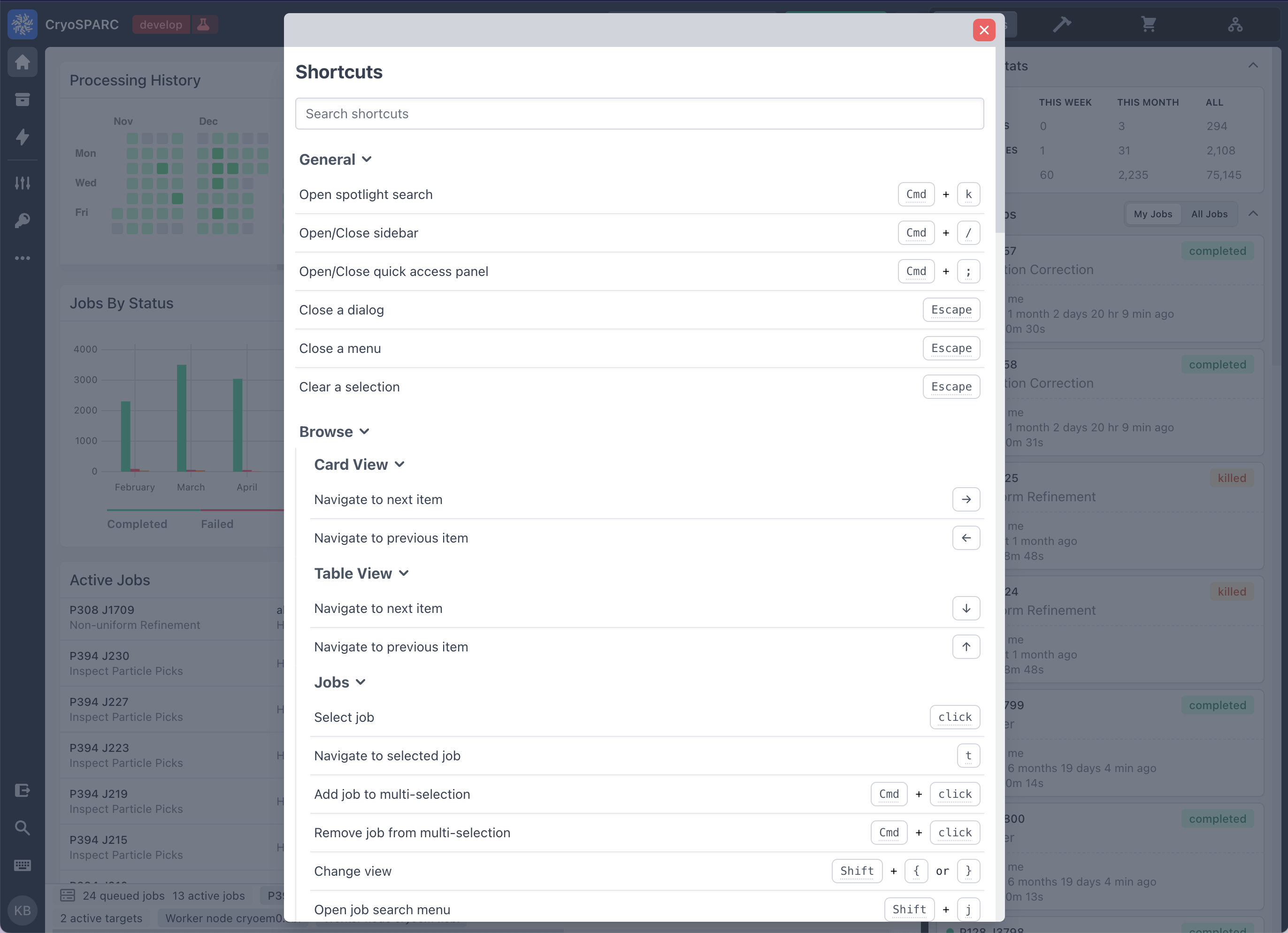
The keyboard shortcut for marking/unmarking a job as final has been modified from 'F' to 'Option + Shift + F'.
Selection menus for projects, workspaces, and sessions have been updated to show all items with no upper limit and no UI performance impact.
Data Cleanup
Added a toggle (default: off) to the Cleanup Data tool that controls whether final-ancestor preprocessing jobs (i.e., preprocessing jobs that are ancestors of jobs marked "final") should be cleared. Preprocessing jobs' outputs (micrographs, particle stacks) take a lot of disk space, but can be reproduced by re-running the jobs again as long as the raw data is available. Therefore, turning on this option can be useful to clear additional space without losing the ability to recreate final results. Read the Data Cleanup guide before proceeding.
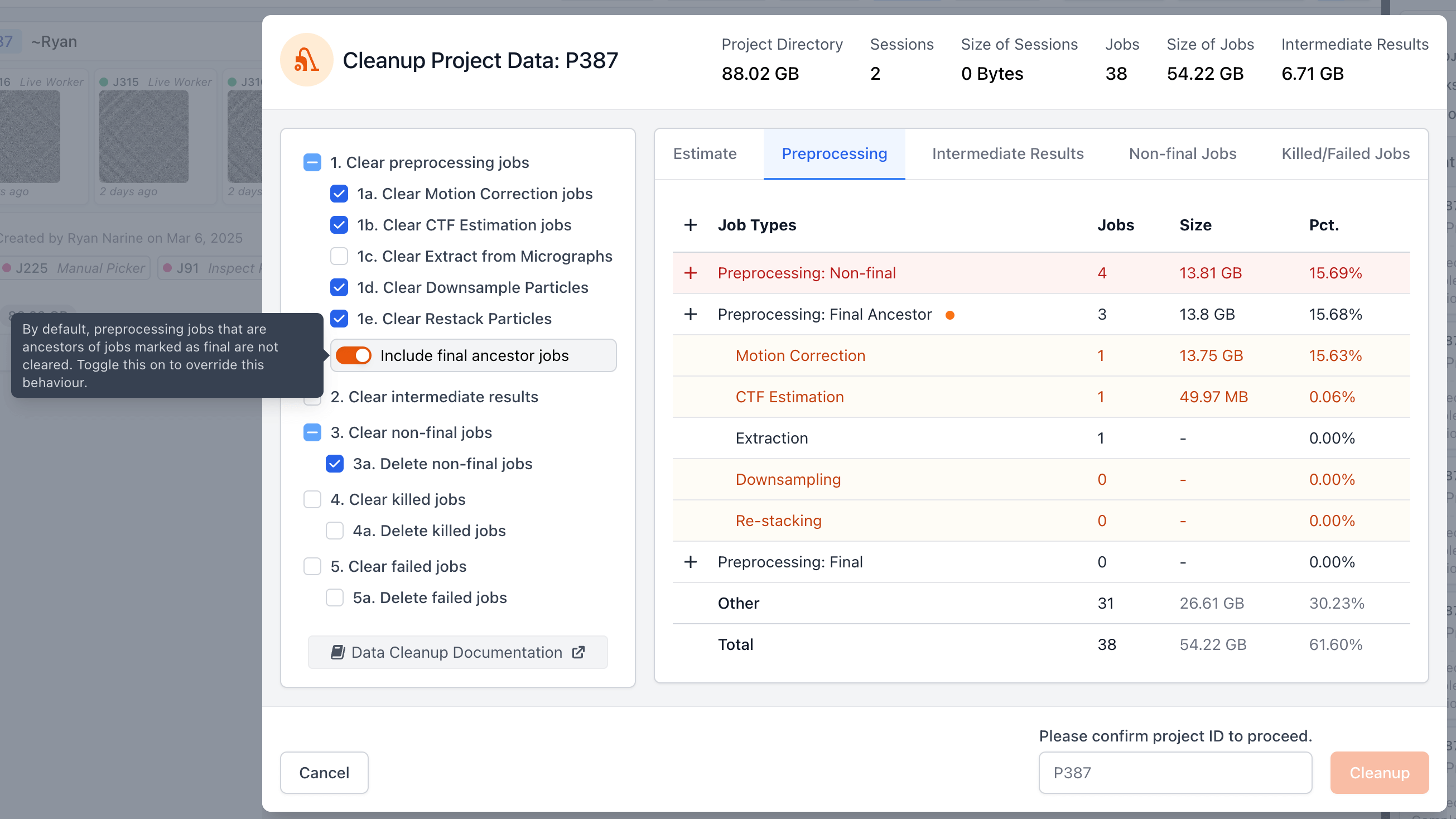
A new command line endpoint delete_output_result_files allows deleting files produced by a job that are part of just a specific result, for example micrographs_non_dw for non-dose-weighted micrographs in Patch Motion Correction.
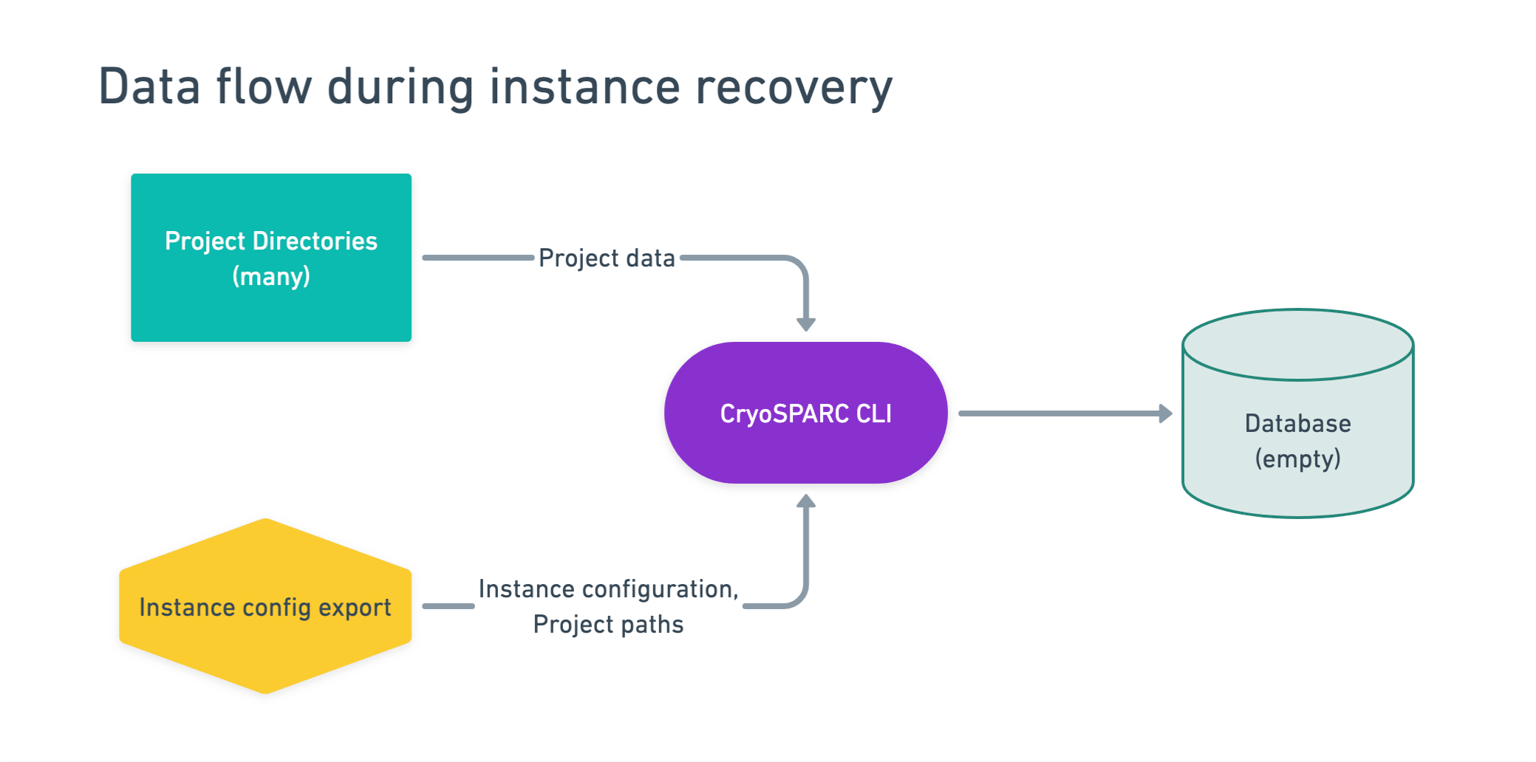
Instance Recovery
Added cryosparcm recover: a simplified way for CryoSPARC instances to fully recover from database loss or corruption without the need for database backups. See the Instance Recovery guide for more details.
Project Attachment and Job Import
When attaching a project, the project card and details sidebar now display the status of the attach process (i.e., in progress, successful, or failed). Projects that fail to attach will display an error banner.
When importing a job, the job card now displays the import status.
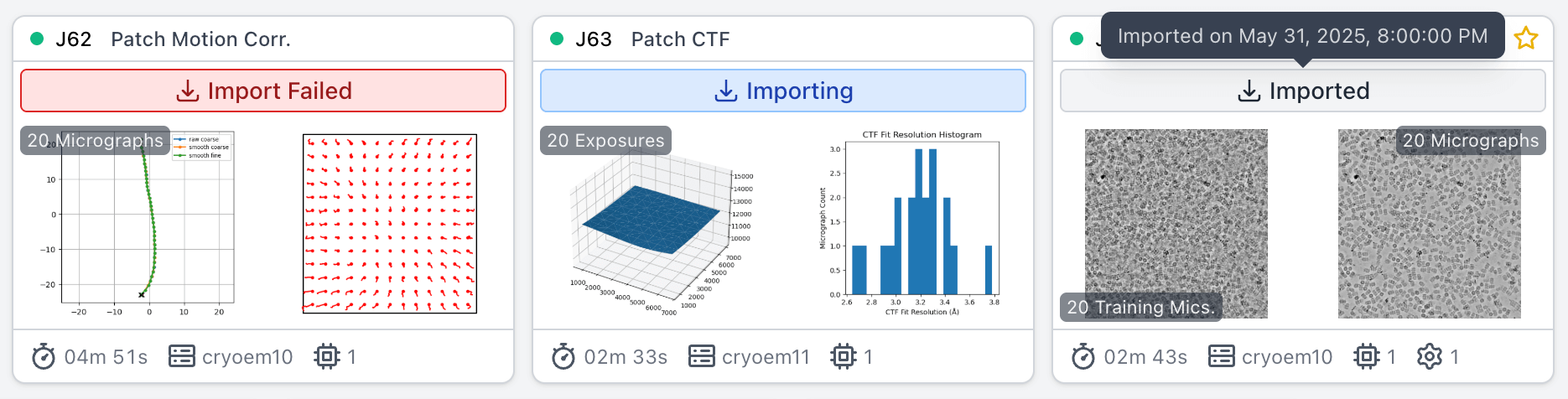
Clear and restart actions are now disabled for imported jobs.
Search and Browse, Job Selection, Navigation
Job search menu can now support viewing and searching any number of jobs in a view without a limit. Menu can be opened with new shortcut shift + j.
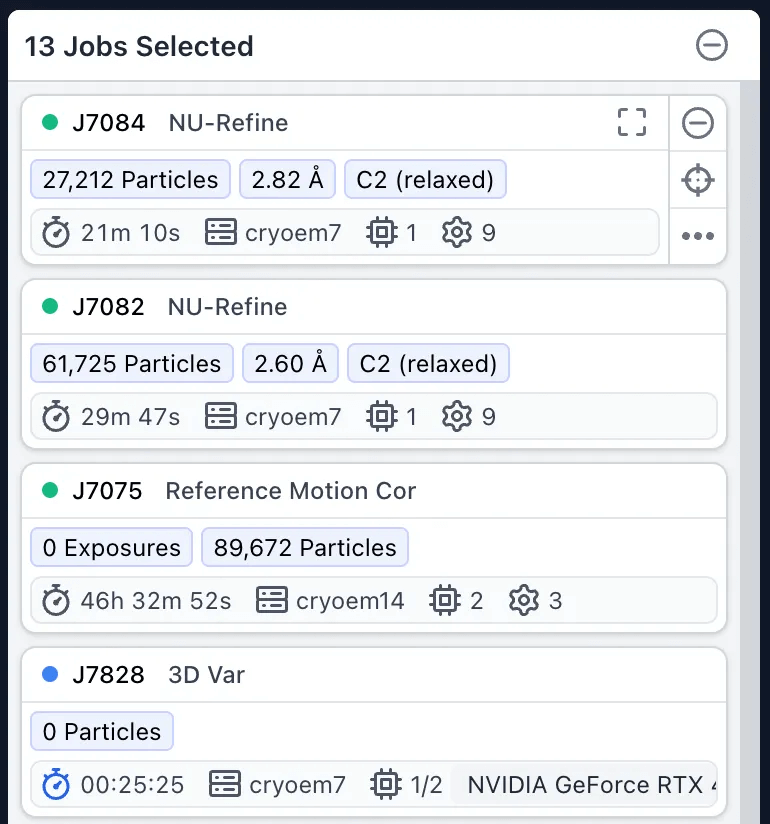
Upgraded multi-selection experience for jobs: identify, navigate to and view a summary of results within the sidebar. Sidebar cards include key information including info tags, runtime, custom parameters and resource usage, as well as actions to open the job dialog, target (go to) the relevant card in the browse view, and open the quick actions menu.
Clicking on a job header within the current jobs tab will open the job preview, similar to the browse views.
The current browse view (card, table, etc.) can now be toggled using the keyboard shortcut shift + { or }.
Resolved an issue when attempting to remove the 'Final or Ancestor of Final' filter within the browse system.
Resolved an issue were jobs of a certain status were not able to be unlinked.
Navigating the job card view using the arrow keys will no longer get stuck on groups.
Resolved an issue where the multi-select quick actions menu would not display when selecting dozens of jobs.
Data Import
Reassign Particles to Micrographs now creates a separate output group for particles that did not match any of the input micrographs, rather than failing.
Import Particle Stack for helical particles now uses randomized filament_uid for each filament (rather than copying directly from rlnHelicalTubeID) to ensure the correct distribution of values.
Import 3D Volumes will no longer fail when importing EMDB volumes with IDs starting with zero.
Tooltip for the gain reference field in Import Movies accurately reflects the fact that TIFF gain references are supported.
Preprocessing
Added a parameter to Patch Motion Correction and Reference Based Motion Correction jobs called "hot pixel threshold". This controls how many standard deviations away from the mean a pixel can be before it is considered a stuck or aberrant pixel, and ignored during motion correction.
Added a parameter to the Micrograph Junk Detector that sets a minimum area for junk labels below which particles won't be rejected.

Fixed a bug in the Micrograph Junk Detector which caused masks to be slightly offset for certain micrograph sizes.
Manually Curate Exposures will no longer fail if zero particles are connected.
In Manually Curate Exposures, the button to toggle display of annotation controls is now only shown when annotations are loaded.
Resolved an issue in Manually Curate Exposures, where the exposure grid view would not update after changing filters.
Particle Picking
Deep Picker Train and Deep Picker Inference have been deprecated and are no longer present in CryoSPARC v5. Previously-run jobs are still visible in the interface.
Blob Picker now includes a warning if the Lowpass filter to apply to templates/micrographs parameter values are too high and incompatible with the specified "Minimum particle diameter" value.
Blob Picker now has two elliptical blob generation modes (stretch and squeeze) to account for different particle shapes, corresponding to thinner rods and flatter disks. It also has a parameter Blob size spacing (A) that controls the number of intermediate sized blobs that will be generated between min and max diameters, and prints the diameters of the circular, elliptical, and ring templates alongside the plots of the templates.
When turning on the "Pick on denoised micrographs" parameter in Template Picker or Filament Tracer, the "Use CTFs to filter the templates" parameter will be set to the correct value automatically.
Topaz Extract, Topaz Train and Cross Validation now have a progress bar during preprocessing. Topaz Train now logs the training status per epoch.
Topaz v0.3.0 is now supported.
Micrographs denoised using the Micrograph Denoiser are now compatible with Topaz v0.3.0.
Topaz jobs using Topaz v0.3.0+ now use a file with a list of micrograph filenames, to avoid "Argument list too long" errors.
Filament Tracer now prints the diameters (if template is not provided) of the filament. Filament tracer and template tracer no longer cause errors due to changes in blob picker parameter.
Particle Curation
Several updates to Subset Particles by Statistic:
- The job now allows for subsetting by either
Per-particle scale (used), which is the value used by the upstream job during back projection of particles, orPer-particle scale (optimal), which is the value computed but not necessarily used by the upstream job. The job defaults toper-particle scale (optimal)as the statistic. - The job now allows for subsetting by the total amount of shift in either 2D or 3D alignments, and also by the azimuth or elevation from 3D alignments.
- The job has a new option to ensure that an equal number of particles are selected from each half-set split defined in the incoming particle stack. The job also allows splitting particle sets into the two gold-standard half-sets based on
alignments3D/split.
Inspect Particle Picks no longer fails when there are too few particles, instead it will skip CTF bins that have zero particles and throw a warning instead.
Fixed issue in Downsample Particles where alignments3D and alignments2D were not being updated, causing the job to produce incorrect results when Recenter using aligned shifts was enabled.
3D Refinement
BILD files are now output for viewing direction distributions in all refinements.
Refinement jobs now include cFAR scores in summary statistics, so that these values are available to scripts using cryosparc-tools.
Fixed issue in Helical Refinement where the Maximum out-of-plane tilt angle parameter value would reset to the default upon launching the job, regardless of its specified value.
Postprocessing and Diagnostics
In Orientation Diagnostics, a new expanded cFSC plot shows all cFSC curves, and raw cFSC data is now output to a csv file in the job directory to facilitate plot reproduction. In addition to cFAR, the job now reports 'tFAR', a variant of cFAR which uses toroidal Fourier segments rather than conical segments. In our testing, tFAR can better represent signal anisotropy under unimodal or bimodal viewing direction distributions. Both tFAR and cFAR scores are more prominently displayed in plots.
Updates to Sharpening Tools:
- The job now allows sharpening without applying an FSC filter. Instead, a Butterworth lowpass filter of custom resolution and order can be specified.
- The job now reads the FSC mask from the
fsc_mask_autoslot in the input volume group. If desired, Sharpening Tools is also able to run without a mask.
Validation (FSC) no longer fails when using the CPU compute facility.
Utility Jobs
In Volume Tools, the default filter is changed to 8th order Butterworth.
Volume Alignment Tools now has a parameter to control whether the mask is multiplied onto the input volume.
Volume Alignment Tools now allows for only applying a mask as a valid action.
Volume Alignment Tools now correctly outputs masks with appropriate pixel size.
Align 3D Maps no longer applies a lowpass filter to outputted maps. A new parameter, Alignment resolution (A), is instead used to control the maximum frequency of information used for volume-to-volume alignment.
Improvements to the alignment algorithm used in Align 3D Maps. The objective function now accounts for overall greyscale differences between maps, which can improve resulting alignments in cases where input volumes came from different processing workflows.
Remove Duplicate Particles now logs the micrograph's pixel size that is used to compute inter-particle distances.
Exposure Group Utilities and other jobs that assign exposure group ids now correctly increment a project-level exposure group counter so that new exposure groups receive a unique id.
Installation and Configuration
CryoSPARC v5's performance benchmarking system is not backwards compatible. New performance benchmarks can be recorded in v5 but will not be retained if downgrading to v4.
CryoSPARC v5 includes updated performance benchmark references on bare metal and AWS nodes.
cryosparcm worker connect and cryosparcm worker disconnect commands can be used to manage connected nodes from the master node. View the updated v5 cryosparcm reference here.
CryoSPARC will now check for conflicts with network ports at installation time.
CryoSPARC will now check for conflicts with active network ports at startup time.
Improved detection for when a scheduler target is the master node.
The default range of logs returned in cryosparcm log and cryosparcm errorreport has been increased from 7 days to 30 days.
Modified cluster launch scripts to append to the job log file instead of overwriting.
Prevent "Could not parse signed file" error during instance startup after changing license IDs.
Fix permissions error when creating job directories on NFS drives.
Worker updates are now copied directly instead of over SSH when updating standalone instances.
System Improvements and Fixes
Notifications for actions and changes within a project are shown to admin users when viewing that project, regardless of who created it and the sharing permissions.
Native browser autocomplete dialogs are disabled when interacting with an autocomplete filter within the interface.
Sort order will now be respected for new jobs created in a workspace sorted by Job ID.
Resolved an issue where flags were not retained when rebuilding a workflow.
Sidebar action panel doesn't scroll on small height windows
Filter hidden parameters out of job card footer widget.
Fixed a bug which could allow a specific kind of movie, micrograph or particle file corruption (truncated frames) to go unreported.
Downstream programs that read MRC files from CryoSPARC and expect them to be in CCP4 format will no longer encounter errors due to checksums embedded in CryoSPARC MRC output files.
3D Variability Display interactive cluster plot legend now matches cluster numbers from job output.
Resolved an issue where the exposure count for Reference Based Motion Correction would always display as 0.